Updated on November 01, 2025 05:33:18 PM
In Haryana’s fast-paced market, protecting your original product design is just as important as creating it. If you’re a fashion business owner or designer with a unique design or pattern, how do you stop others from copying your work? That’s where design registration comes in.
Design registration, governed by the Design Act of 2000, is a form of Intellectual Property Right (IPR) that protects the visual appearance of a product—its shape, pattern, color combination, or configuration, whether 2D or 3D. Unlike patents or trademarks, which cover functionality or brand identity, design registration secures how your product looks.
For entrepreneurs and designers in Haryana, registering your design is a smart way to stay ahead of competitors and protect your brand. However, the process can be tricky—especially if you're unfamiliar with legal steps. From choosing the right class to filing the statement of novelty, every step matters.
If you’re planning to register your design in Haryana and need expert support, our team at Litem Legalis is here to help. We simplify the process and ensure your design gets the protection it deserves. Contact us today to safeguard your work from infringement.
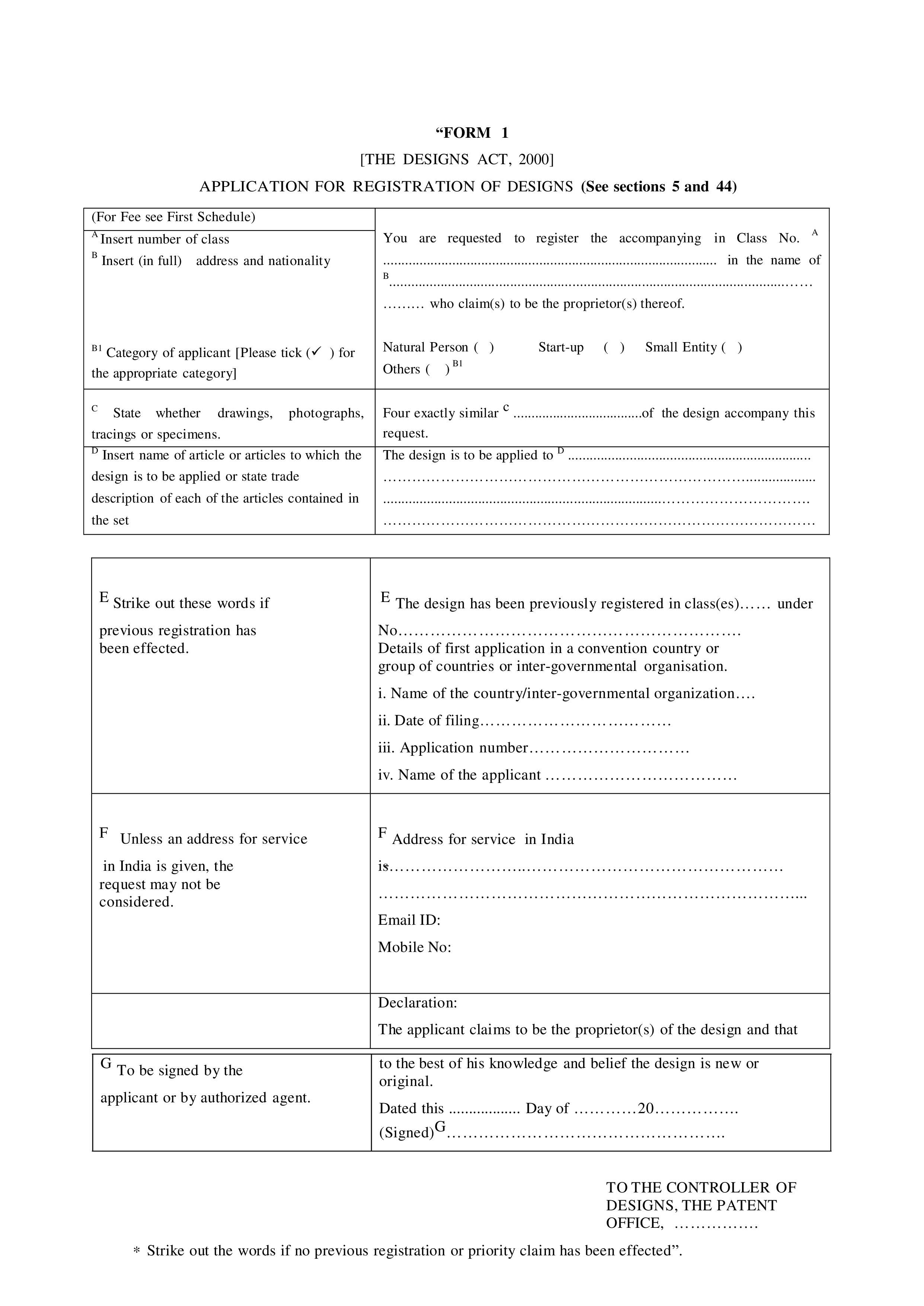
Design registration in Haryana is a legal right that safeguards the new visual aspect of a product. When you have created a product with a unique shape, pattern, or configuration, registering it will prevent others from copying or using it without your permission. This right is given under the Design Act of 2000 and serves to protect the owner with exclusive rights to use, sell, or license the design for 10 years, with an extension of 5 more years.
For businesses, startups, and designers based in Haryana, design registration not only prevents duplication but also brings value addition to the brand and market position. It specifically safeguards:
A design under IPR regulations refers to the visual elements of a product including its shape configuration pattern and colors. The design can exist as either a two-dimensional drawing or a three-dimensional model as long as it presents an visual aspect.
For Example : A unique torchlight shape can become eligible for registration. You can only protect design through appearance because functionality remains outside the scope of protection. A physical object called an article requires the design to be transformed through industrial or manual processes.
The following elements do not qualify as design elements: The product's operational mechanics together with trademarks and artistic works protected by copyright law are excluded from design protection.
To qualify for Industrial design registration eligibility(also know as a design patent) demands that your design satisfies these requirements to receive legal protection which grants you exclusive rights for its use and sale or licensing. An industrial design requires three essential requirements to qualify for registration.
Design registration offers key benefits to help safeguard and strengthen your brand:
Following steps are mentioned below which need to be undergo while obtaining Trademark Registration:
Before sharing your design with manufacturers, investors, or designers, ask them to sign an NDA (Non-Disclosure Agreement). This prevents them from using or copying your design without permission.
Before applying for design registration, it is essential to verify that your design is unique and not already registered. This helps avoid legal issues and ensures that your design isn’t already registered.
How to Check for Similar Designs:
If you cannot find a similar registered design, you may proceed with filing a request for a Prior Art Search (Form-7) along with a fee of ₹1,000.
Once you confirm that your design is new, You’ll prepare your design application in which you need to show your design in 7 views: perspective (overall), top, bottom, front, rear, left side, and right side. Use software like SolidWorks if you want a 3D model, or draw it by hand. Put each view on an A4 sheet (up to 7 sheets total) and include:
Once you have confirmed the uniqueness of your design and peapre the design applciation, the next step is to file the design application with the Haryanan Patent Office through the IP Haryana e-filing system.
Head to ipHaryana.gov.in, find the e-filing design section, and click “New User Sign Up.” Choose your applicant type:
Fill in Details – Enter your name, address, and other required information.
Upload E-Signature – Authenticate your application with an e-signature.
Submit & Confirm – Complete the process and receive a confirmation email.
After filing, the Design Office will examine your application. If they find any issues, they will send a First Examination Report (FER). You need to respond within 3 months to clarify or correct any objections.If the examiner has further doubts, they may schedule a hearing where you (or your lawyer) can explain your case.After filing, the Design Office will examine your application. If they find any issues, they will send a First Examination Report (FER). You need to respond within 3 months to clarify or correct any objections.If the examiner has further doubts, they may schedule a hearing where you (or your lawyer) can explain your case.
Once all objections are resolved, the Design Office will approve your application and issue a Design Registration Certificate. This certificate proves your legal ownership of the design.
Here’s a list of documents required for a design application:
Registering a design in Haryana involves specific government fees, which vary based on the applicant type—individuals, small entities, and others (companies, firms, etc.). The fee structure is outlined under the Designs Act, 2000 and its related rules
| S.No. | Purpose | Form No. | Fees (INR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Application for design registration (Sections 5 & 44) | Form-1 | 1,000 |
| 2 | Claim to proceed as an applicant or joint applicant (Section 8) | Form-2 | 500 |
| 3 | Application for extension of copyright (Section 11) | Form-3 | 2,000 |
| 4 | Application for restoration of lapsed design (Section 12) | Form-4 | 1,000 |
| 5 | Additional fee for restoration | - | 1,000 |
| 6 | Inspection of a registered design (Section 17) | Form-5 | 500 |
| 7 | Request for information on a design (when registration number is given) (Section 18) | Form-6 | 500 |
| 8 | Request for information on a design (when registration number is not given) | Form-7 | 1,000 |
| 9 | Petition for cancellation of a registered design (Section 19) | Form-8 | 1,500 |
| 10 | Notice of intended exhibition/publication of an unregistered design (Section 21) | Form-9 | 500 |
| 11 | Application for document registration in the Design Register (Section 30) | Form-10 | 500 |
| 12 | Additional fee for each extra design in the same application | - | 200 |
| 13 | Application for entry of name of proprietor or part proprietor in the Register of Design (Section 30) | Form-11 | 500 |
| 14 | Application for mortgage or license entry | Form-12 | 500 |
| 15 | Entry of notification of a document in the Design Register (Section 30 & Rule 37) | Form-13 | 500 |
| 16 | Request for correction of clerical errors (Section 29) | Form-14 | 500 |
| 17 | Request for certification (Section 26 & Rule 41) | Form-15 | 500 |
| 18 | Application for certified copy of a registered design (Section 17) | Form-16 | 500 |
| 19 | Application for rectification of the Register of Design (Section 31) | Form-17 | 500 |
| 20 | Application for an extension of time to submit priority documents (Rule 15 & Rule 18) | Form-18 | 200 per month |
| 21 | Notice of opposition (Rule 40) | Form-19 | 100 |
| 22 | Notice of intention to attend a hearing (Rule 29 & 40) | Form-20 | 500 |
| 23 | Authorization of an agent or other person | Form-21 | No fee |
| 24 | Request for altering name/address in the Register of Design | Form-22 | 200 |
| 25 | Request for entering two addresses in the Register of Design | Form-23 | 200 |
| 26 | Petition for amendment of any document (Rule 46) | - | 500 |
| 27 | Petition for enlargement of time (Rules 29, 40, 47) | - | 500 |
| 28 | Inspection of the Register of Design (Rule 38) | - | 250 |
| 29 | Petition not otherwise provided for | - | 1,000 |
| 30 | Claiming small entity status | Form-24 | No fee |
When it come to patent protection, people tend to mix up design patents with utility patents although these patents protect distinct aspects of inventions. The legal protection offered by both patents exists but applies to different elements of an invention.
In some cases, a product may qualify for both patents. For example, an innovative smartwatch might have a distinctive outer design (covered by a design patent) and a groundbreaking health-monitoring algorithm (protected by a utility patent).
Understanding these differences helps businesses and inventors make the right choice when seeking patent protection.
In conclusion, protecting your design in Haryana through design registration creates legal safeguards that also build your business strength for future growth. The competitive business environment in Haryana benefits from design exclusivity due to which manufacturers achieve market dominance while dimoralize product replication. The unique element of your creativity needs protection since it stands as your biggest differentiator.
At Litem Legalis our experts can assist you with design registration in Haryana. We simplifies and streamlines design registration for clients through their team of legal and intellectual property professionals. We welcome your call at this moment and offer comprehensive design protection services with complete assurance.

Legal Consultation

Expert Lawyers

Lowest Fees

Quick Process
Design registration is a legal process that protects the visual appearance of a product—including its shape, configuration, pattern, and ornamentation—granting the owner exclusive rights for up to 10 years (extendable to 15 years).
Design registration offers several important benefits for businesses and creators:
It helps protect your design, grow your brand, and add business value.
Once granted, design registration offers exclusive rights for 10 years, with the option to extend protection for an additional 5 years.
Essential documents include the application form (Form-1), multiple views of the design (as per the guidelines), a power of attorney if applicable, and additional forms such as Form-24 for small entity status, along with any priority or assignment documents if required.
Disclaimer: The content provided on this site is intended for informational purposes only. Accessing or utilizing this site and its materials does not establish an attorney-client relationship. The information contained herein does not constitute legal or professional advice and should not be relied upon as such. It is not a substitute for obtaining legal counsel from a qualified attorney licensed in your jurisdiction.